General Linux
Questions answered
How to emulate mouse on USB?
-
echo -e -n '\x0\x7f\x7f\x0' > /dev/hidg1
This moves the mouse 127 pixels to the right and 127 pixels down (7f is hex for 127)echo -e -n '\x0\x81\x81\x0' > /dev/hidg1
This moves the mouse 127 pixels to the left and 127 pixels up (81 is hex for -127). Do not enter x80 as I think this is effectively negative 0 or whatever. So to get other negative numbers you keep going e.g 82 is -126, 83 is -125 etc
- How to control PC Mouse from Pi Zero through USB describes and alternative to use Linux-USB Gadget API Framework.
- Script which creates a HID gadget, another script, another script, another script.
 The script must be run before plugging the device into a host.
The script must be run before plugging the device into a host.
Additionally:
- Turning your Raspberry PI Zero into a USB Gadget is very nice guide about how to enable serial & Ethernet gadget mode. Although the article reads that RNDIS driver is installed for
RNDIS/Ethernet Gadget, however if that does not happen then install standardRemove NDIS Compatible Deviceas to How to install Microsoft RNDIS driver for Windows 7. - Raspberry Pi Zero OTG Mode enumerates and shortly describes different gadget modules
gadget_hid.txtdocumentation from Linux Kernel with C-program example.
How to uninstall program which was installed using make install?
checkinstall.
How to fix cron syslog entry Authentication service cannot retrieve authentication info
CRON: Authentication service cannot retrieve authentication info
pwck command, as your /etc/passwd is not in sync with /etc/shadow.
How to capture kernel panic log?
netconsole kernel module as log transmitter and rsyslog as log receiver on some remote system (e.g. booted as life image). Check Setup netconsole to capture kernel panic logs. Step-by-step instruction:- Create
/etc/modprobe.d/netconsole.conf
# Enable remote kernel logging. # netconsole=<LOCAL_PORT>@<SENDER_IP_ADDRESS>/[SENDER_INTERFACE],<REMOTE_PORT>@<RECEIVER_IP_ADDRESS>/[MAC_ADDRESS] options netconsole netconsole=6666@192.168.5.1/br0,514@192.168.5.100/
Note that MAC address is optional, however trailing slash is obligatory.
- Do
modprobe netconsole– it should result the following indmesg:netpoll: netconsole: local port 6666 netpoll: netconsole: local IPv4 address 192.168.5.1 netpoll: netconsole: interface 'br0' netpoll: netconsole: remote port 514 netpoll: netconsole: remote IPv4 address 192.168.5.100 netpoll: netconsole: remote ethernet address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff console [netcon0] enabled netconsole: network logging started
If module fails with the messagenetpoll: (null): eth1 doesn't support polling, abortingthen remove the conflicting interface from the bridge. - After that on remote PC (192.168.5.100) run
nc -lu 514 | tee -a dmesg.logto capture kernel messages.
See also:
- Kdump – mechanism to dump machine memory content on kernel crash (enabled in Debian kernels)
- systemd in action – оценка устойчивости нативного формата БД к произвольным повреждениям, рассмотрение возможности
journaldпо передаче логов по сети- Remote logging is not available in Debian Jessie, see Enable systemd-journal-remote.
How to capture core dumps?
How to format dmesg timestamps?
/proc/uptime needs to be added:
dmesg | perl -w -Mstrict -MPOSIX -e 'my $uptime = $1 if `cat /proc/uptime` =~ /^(\d+)\./;
foreach my $line (<>) {
printf($line =~ /^\[\s*(\d+)\.\d+\](.+)/
? "[" . strftime("%F %T", localtime(time() - $uptime + $1)) . "]$2\n"
: $line
);
}'
Or simply use dmesg -T.
See Convert dmesg timestamp to custom date format and How to convert 'dmesg' time format to 'real' time format.
How to view boot log of the previous system run?
/var/log/boot in systemd-based distributive, as they are managed by journalctl. However the last one does not flush logs into persistent location. In order to force that, set Storage=persistent in /etc/systemd/journald.conf and run systemctl restart systemd-journald. After that you will be able to see logs for boots in the past (performed after the option was applied):
# journalctl --list-boots # journalctl -b1 -o short-precise
How to list all failed systemd units?
systemctl list-units –failed
To further see the last log messages of failed unit:
systemctl -l status some-failed.service
How to debug the problem related to service order execution?
# systemd-analyze verify default.target
should not display something like that:
Found ordering cycle on systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service/start Found dependency on local-fs.target/start Found dependency on problematic.service/start Found dependency on sysinit.target/start Job systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service/start deleted to break ordering cycle starting with sysinit.target/start
# systemctl show -p Requires,Wants,Requisite,BindsTo,PartOf,Before,After problematic-service.target # systemd-analyze dot problematic-service.target other.target | dot -Tsvg > cycle.svg
MySQL does not stop under systemd
How to set up a runlevel in Debian?
- Works for all environments: edit
/etc/default/gruband add3to the end of kernel line:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet 3". Refresh grub (runupdate-grub). - For SysV init edit
/etc/inittaband set value3to 2nd column of the line i.e.id:3:initdefault: - For
systemd-driven environment runcd /etc/systemd/system && ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target default.target
How to program what power button does?
systemd. Edit /etc/systemd/logind.conf and set e.g.
[Login] HandleLidSwitch=ignore HandleLidSwitchDocked=ignore
to ignore closing the notebook lid or
[Login] HandlePowerKey=ignore
to ignore power button press and then run service systemd-logind restart.
See also:
/etc/acpi/events/powerbtn-acpi-support and comment the action.
How to save battery power on Laptop?
What is ASPM?
- ASPM feature can be configured by BIOS or by OS.
- Check the report generated by
fwtsutility (currently missing in Debian, hence download and install packagesfwts,libfwts1,libfwtsacpica1,libfwtsiasl1,fwts-efi-runtime-dkms). The following report shows that ASPM is not supoprted:
# fwts aspm; cat report.log Test 1 of 2: PCIe ASPM ACPI test. SKIPPED: Test 1, No valid FACP information present: cannot test ASPM. Test 2 of 2: PCIe ASPM registers test. WARNING: Test 2, RP 0000h:00h:1Ch.00h L0s not enabled. WARNING: Test 2, Device 0000h:01h:00h.00h L0s not enabled. ADVICE: The ASPM L0s low power Link state is optimized for short entry and exit latencies, while providing substantial power savings. Disabling L0s of a PCIe device may increase power consumption, and will impact the battery life of a mobile system. PASSED: Test 2, PCIe ASPM setting matched was matched. WARNING: Test 2, RP 0000h:00h:1Ch.03h L0s not enabled. WARNING: Test 2, Device 0000h:03h:00h.00h L0s not enabled. ADVICE: The ASPM L0s low power Link state is optimized for short entry and exit latencies, while providing substantial power savings. Disabling L0s of a PCIe device may increase power consumption, and will impact the battery life of a mobile system. PASSED: Test 2, PCIe ASPM setting matched was matched.
See also:
How to list all libraries loaded by a process?
pldd <pid> or pmap 6297 | grep .so | cut -c24- | sort -u
Where is X11 session autostart?
- When starting VNC server then
~/.vnc/xstartupotherwise~/.xsessionrc(~/.Xtigervnc-sessionfor TigerVNC), see Xsession and Autostarting. - Xfce session is stored in session cache in
./.cache/sessions/xfce4-session-*and managed from Settings → Session and Startup → Session tab.
Where is desktop autostart?
.config/autostart or .kde/Autostart directory.
How to send POST HTTP request using cURL?
curl -X POST --header "Content-Type:text/xml" -d @filename.xml http://example.com/path/to/resource
Another example with:
-sto disable progress indicator-vto print headers (is better than-D -)–rawto see original (not decoded) message, e.g. when the message is chunked–negotiate -u :to enable SPNEGO authentication
curl -s -v --raw --negotiate -u : -X POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'Accept: application/json' -d '{ "field": 1 }' 'http://server.org/path'
How to force diff to ignore different newline presentation (CR/LF)?
--ignore-all-space option:
diff --ignore-all-space file1 file2
How to remove BOM from the text file?
''cut -c'' (''--characters'') does not work with UTF-8
$ echo 'αβγ' | cut -c 3-4 β
Console
How to disable printing of kernel messages to console?
dmesg -n 1 or (for recent versions) dmesg -D
How allocate tty1 to display syslog output?
- Run
systemctl stop getty@tty1.servicethensystemctl disable getty@tty1.service - Uncomment/add the following to
/etc/systemd/journald.conf
ForwardToConsole=yes TTYPath=/dev/tty1 MaxLevelConsole=info
Didn't work:
Change ACTIVE_CONSOLE="dev/tty[2-4]" in /etc/default/console-setup and run dpkg-reconfigure console-setup, see:
How to disable cleaning of first console after boot?
In /etc/inittab add the --noclear option for the configuration line (starts with c1) of first virtual console:
c1:2345:respawn:/sbin/agetty --noclear -8 38400 tty1 linux
For systemd check Stop Clearing My God Damned Console:
# mkdir /etc/systemd/system/getty@.service.d # cat > /etc/systemd/system/getty@.service.d/noclear.conf <<'EOF' [Service] TTYVTDisallocate=no EOF # systemctl daemon-reload
How to enable monitor standby in console?
setterm –blank 2
How to monitor the progress of byte-stream copy?
dd if=/dev/urandom | pv | dd of=/dev/null- Rub
ddin one console and in another runkill -USR1 $(pgrep ^dd)
Alternative is progress – Linux tool to show progress for cp, mv, dd, … which monitors open filedesciptors in /proc to display the progress.
How to control coloring of ls output?
export LS_COLORS='no=00:fi=00:di=05;33:ln=01;36:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:r=40;31;01:ex=01;32.tar
How to recover occasionally deleted tmux pipe / session?
If the socket is accidentally removed, the SIGUSR1 signal may be sent to the tmux server process to recreate it.
So sending the signal and attaching works:
$ killall -s SIGUSR1 tmux $ tmux attach
How to fix the problem with missing locale?
perl: warning: Please check that your locale settings:
LANGUAGE = "en_US:en",
LC_ALL = (unset),
LC_MESSAGES = "en_US.UTF-8",
LANG = "en_US.UTF-8"
are supported and installed on your system.
- Check that
/etc/default/localehas a correct locale setting. If not, runupdate-locale LANGUAGE=en_US.UTF-8to update it. - Check that desired locale
en_US.UTF-8is present in/etc/locale.gen(grep en_US.UTF-8 /etc/locale.gen). If not, runlocale-gen en_US en_US.UTF-8 && dpkg-reconfigure localesto generate it.
Security
Strange log message from pam_ldap
pam_ldap module correctly, but still this lines in log filesshd[29284]: pam_ldap: error trying to bind as user "cn=jack,cn=users,dn=domain" (Invalid credentials)
libnss-ldap is installed and configured correctly.
How to implement LDAP-based authentication?
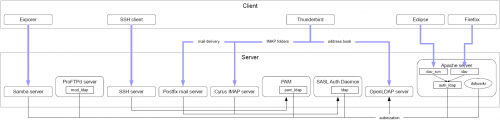
This is currently implemented only in Apache mod_authnz_ldap module. You need to enable Require valid-user and Require ldap-group. After reading the following documentation on search filtering (String Representation of Search Filters, LDAP: Matching Rule Identifier, LDAP Attribute Syntax Definitions, LDAP Search Filters1), Правила соответствия) and trying to find the extended matching rule (like this2), I came to the conclusion that this search cannot be done via one filter. During the first search the module should learn the dn of a user by it's uid or email, and then use the located dn to search in a specific group. To make things more simple I suggest to define dummy object classes to define a list of authorized services and use this object class in a filter. Examples:
LDAP schema (/etc/ldap/schema/centurion.schema)
objectclass ( 1.3.6.1.4.1.1000.0 NAME 'commonAccount' SUP top ABSTRACT
DESC 'General account account'
MUST ( uid $ userPassword ) )
objectClass ( 1.3.6.1.4.1.1000.1 NAME 'apacheAccount' SUP commonAccount AUXILIARY
DESC 'Apache htpasswd account' )
objectClass ( 1.3.6.1.4.1.1000.2 NAME 'dokuwikiAccount' SUP commonAccount AUXILIARY
DESC 'Dokuwiki account' )
objectClass ( 1.3.6.1.4.1.1000.3 NAME 'mailAccount' SUP commonAccount AUXILIARY
DESC 'Cyrus/Postfix account' )
objectClass ( 1.3.6.1.4.1.1000.4 NAME 'proftpdAccout' SUP commonAccount AUXILIARY
DESC 'ProFTPd account' )Apache mod_authnz_ldap (/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/001-default-ssl)
<IfModule mod_authn_alias.c> <AuthnProviderAlias ldap ldap-auth-provider> AuthLDAPURL "ldap://localhost:389/cn=persons,cn=centurion?uid?one?(objectClass=apacheAccount)" </AuthnProviderAlias> </IfModule> <VirtualHost _default_:443> Alias /dav/ /var/lib/dav/ <Location /dav> DAV on AuthType Basic AuthName "DAV Storage" AuthBasicProvider ldap-auth-provider Options Indexes <LimitExcept GET HEAD OPTIONS> Require valid-user </LimitExcept> </Location> </VirtualHost>
dokuwiki auth_ldap (conf/dokuwiki.php)
$conf['useacl'] = 1; $conf['autopasswd'] = 0; $conf['authtype'] = 'chained'; $conf['auth']['chained']['authtypes'] = 'plain,ldap'; $conf['auth']['ldap']['server'] = 'ldap://localhost:389'; $conf['auth']['ldap']['usertree'] = 'cn=persons,cn=centurion'; $conf['auth']['ldap']['userfilter'] = '(&(objectClass=dokuwikiAccount)(uid=%{user}))'; $conf['auth']['ldap']['grouptree'] = 'cn=groups,cn=centurion'; $conf['auth']['ldap']['groupfilter'] = '(member=%{dn})'; $conf['auth']['ldap']['version'] = 3; $conf['passcrypt'] = 'ssha'; $conf['defaultgroup']= 'dokuwiki';
Similar ProFTPd topics: 1, 2, 3. Also take in mind this bug, which effectively breaks the authentication via LDAP, and which was solved in proftpd-basic_1.3.2-1.
ProFTPd mod_ldap (/etc/proftpd/ldap.conf)
<IfModule mod_ldap.c> LDAPServer ldap://localhost LDAPSearchScope onelevel LDAPDoAuth on "cn=persons,cn=centurion" "(&(objectclass=proftpdAccount)(uid=%v))" LDAPAuthBinds on </IfModule>
Samba server can be switched to using LDAP the following way3):
Samba configuration (/etc/samba/smb.conf)
passdb backend = ldapsam:ldap://localhost ldap suffix = cn=centurion ldap user suffix = cn=persons,cn=centurion ldap group suffix = cn=groups,cn=centurion # The password for this user is stored in secrets.tdb. It is set by running 'smbpasswd -w passwd': ldap admin dn = cn=ldapadmin,cn=centurion
Samba should have permissions to add sambaSamAccount object class to existing person and initialize needed attributes.
Cyrus IMAP sevice authenticates itself via saslauthd:
ldap_servers: ldap://localhost ldap_search_base: cn=persons,cn=centurion ldap_filter: (&(objectClass=mailAccount)(uid=%u)) ldap_scope: one
base cn=centurion uri ldap://127.0.0.1/ ldap_version 3 rootbinddn cn=ldapadmin,cn=centurion scope sub pam_filter objectClass=shadowAccount pam_password exop nss_base_passwd cn=persons,cn=centurion?one nss_base_shadow cn=persons,cn=centurion?one nss_base_group cn=groups,cn=centurion?one
PAM is configurable via pam-auth-update. Generally you have to add pam_ldap.so to your PAM configuration (see /usr/share/doc/libpam-ldap/examples/pam.conf).
Also you should take in mind, that if some services need the availability of user ID at startup, they need to start after LDAP server. For example, for cron one should add the following lines to init.d script:
... ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: cron ... # Should-Start: slapd # Should-Stop: slapd ...
How to add schemas to OpenLDAP?
- Stop OpenLDAP server:
/etc/inid.d/slapd stop - Create file
schema_import.conflike this:include /etc/ldap/schema/core.schema include /etc/ldap/schema/cosine.schema include /etc/ldap/schema/nis.schema include /etc/ldap/schema/inetorgperson.schema include /etc/ldap/schema/mozilla.schema include /etc/ldap/schema/samba.schema
- Run
slaptestto convert*.schemato*.ldif:
mkdir /tmp/ldap_import; slaptest -f schema_import.conf -F /tmp/ldap_import - Copy necessary files to
/etc/ldap/slapd.d/cn=config/cn=schemagiving them correct numbering:
mv /tmp/ldap_import/cn={4}mozilla.ldif /etc/ldap/slapd.d/cn\=config/cn\=schema\cn\={5}mozilla.ldif
mv /tmp/ldap_import/cn={5}samba.ldif /etc/ldap/slapd.d/cn\=config/cn\=schema\cn\={6}samba.ldif
- Start OpenLDAP server:
/etc/inid.d/slapd start
How to add index to the database in OpenLDAP?
memberUid for the database {1}mdb:
# ldapmodify -H ldapi:// -Y EXTERNAL <<'EOF'
dn: olcDatabase={1}mdb,cn=config
add: olcDbIndex
olcDbIndex: memberUid eq
EOF
SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth
SASL SSF: 0
modifying entry "olcDatabase={1}mdb,cn=config"
To verify check slapcat -s olcDatabase={1}mdb,cn=config output.
How to fix the error "ldif_read_file: checksum error" in OpenLDAP?
- Copy the given
.ldiffile and remove the header lines (auto-generated comments):# AUTO-GENERATED FILE - DO NOT EDIT!! Use ldapmodify. # CRC32 61e6182a
- Calculate CRC32 using
crc32utility fromlibarchive-zip-perlpackage (see How to check crc of a file?). - Put the resulting value into the header of original
.ldiffile.
Note that from v2.4.23-3 the configuration of OpenLDAP has been changed to LDIFF in /etc/ldap/slapd.d, see OpenLDAP Setup.
passwd command fails
passwd command fails with the following message: # passwd someuser passwd: Authentication information cannot be recovered passwd: password unchanged
ldapsearch -x -ZZ fails with a following error: ldap_start_tls: Connect error (-11)
ldap_sasl_bind(SIMPLE): Can’t contact LDAP server (-1)
Unknown certificate results:
ldap_start_tls: Connect error (-11)
ldapsearch -h your.server.fqdn -x -d 127 -LLL -ZZ. If it says TLS: peer cert untrusted or revoked then it means the server returns the certificate, which cannot be verified by the client. To fix do the following:- Appended necessary certificate to that file (
cat my.crt >> /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt)6)
Alternatively one can add TLS_REQCERT never to his ~/.ldaprc.
slapd daemon fails to start with message main: TLS init def ctx failed: -1
olcTLSCertificateFile and olcTLSCertificateKeyFile point to readable by OpenLDAP user file (e.g. readable by group openldap).
Network and wireless
How to rename network interfaces?
- Using udev rules
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", ATTR{address}=="00:37:e9:17:64:af", KERNEL=="eth?", NAME="eth0" # MAC of first NIC in lowercase ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="net", ATTR{address}=="00:21:e9:17:64:b5", KERNEL=="eth?", NAME="eth1" # MAC of second NIC in lowercaseOn Debian run for example
INTERFACE=eth0 MATCHADDR=00:01:80:66:5c:68 /lib/udev/write_net_rules - Using modules configuration. Create
alias eth0 tg3 alias eth1 e1000
and run
update-modulesto update/etc/modules.conf. - On modern distros because of predictable network interface names introduction the best way to rename interface is systemd.link (/etc/systemd/network), i.e. create the following file:
/etc/systemd/network/11-net.link
[Match] MACAddress=00:a0:de:63:7a:e6 [Link] Name=eth0
 To reload udev rules run
To reload udev rules run udevadm control --reload-rules && udevadm trigger
 To monitor events, use
To monitor events, use udevadm monitor -e
 To rename interface use
To rename interface use ip link set wlp1s0 name wlan0
References:
- Writing udev rules (local copy (234.43 KiB, 642 downloads))
How to create a bi-directorial link between TCP socket and serial line?
What does RUNNING in ifconfig output mean?
How to implement source-based routing?
eth1 however interface could have other IP address. From command line this is done like this:# echo -e "1\teth1.route" >> /etc/iproute2/rt_tables # ip rule add from 192.168.1.10 table eth1.route # ip route add default via 192.168.1.200 dev eth1 table eth1.route
and corresponding Debian setting is:
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.1.10
up ip rule add from 192.168.1.10 table eth1.route
up ip route add default via 192.168.1.200 dev eth1 table eth1.route
What is the flow of the packets in iptables?
How to offer a proxy server via DHCP?
option wpad-config code 252 = text;
...
subnet 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 {
...
option wpad-config "http://your.web.server/wpad";
}function FindProxyForURL(url, host) { if (shExpMatch(host, "192.168.*") || shExpMatch(host, "127.*") || shExpMatch(host, "localhost") || shExpMatch(host, "*.domain.local") || shExpMatch(host, "*.home") || isPlainHostName(host) || dnsDomainIs(host, ".domain.local")) { return "DIRECT"; } if (isInNet(host, "192.168.0.0", "255.255.0.0")) { return "DIRECT"; } return "PROXY your.proxy.server:3128; DIRECT"; }
How to generate QR code for WiFi network connection?
qrencode -l M -m 0 -o wifi.png "WIFI:S:<SSID>;T:<WEP|WPA>;P:<password>;;"
How to improve WiFi performance?
- Use the channel the interferes less with neighbouring AP:
iwconfig wlan0 channel 11 - Split packets into smaller sizes:
iwconfig wlan0 frag 256 - Switch off rts handshaking:
iwconfig wlan0 rts 1 - Increase the number of retries:
iwconfig wlan0 retry 30 - Don't request or claim the address by ARP:
dhdpcd -A wlan0
References:
What are the WiFi USB dongles that support master mode?
- On Comparison of open-source wireless drivers sort by column Master (AP) mode.
- On drivers page set dropdown box in column AP to “yes”.
Does Realtek RTL8187 support master mode?
When trying to set the card to AP mode the following error is returned:
# iwconfig wlan0 mode master
Error for wireless request "Set Mode" (8B06) :
SET failed on device ra0 ; Invalid argument.
meaning that the card doesn't support master mode. However Aircrack Realtek RTL8187L ieee80211-based driver (but README.FIRST in r8187b-2.6.25-hirte.tar.bz2 reads that driver is for RTL8187B) claims that it supports AP. There are same rtl8187 driver sources which are adapted for Linux 3.8.
Other notes from maillists below:
- RTL8187L chip only has a single hardware transmit queue and the work of getting the high-priority traffic, such as beacons, transmitted at the correct time would be much more than it would be worth. Will the device be able to transmit beacons with an appropriate timing accuracy?
- The module in kernel is using mac80211 wireless stack while the module from Realtek website does not use it.
- To modify the driver, you will need to study some other driver that does work in master mode.
- There were some discussion a while back that some generic master mode support for all mac80211-based drivers might eventually happen.
References:
Error when trying to switch Atheros card to master mode
# iwconfig wlan0 mode master
Error for wireless request "Set Mode" (8B06) :
SET failed on device wlan0 ; Invalid argument.
 Information below is outdated as
Information below is outdated as ath5k module supports master mode (AP).
ath_pci module, which can be build using module-assistant:# module-assistant prepare # module-assistant auto-install madwifi
The modules priorities are configured in /etc/modprobe.d/madwifi:
blacklist ath5k options ath_pci autocreate=ap
The bridge interface is configured as following in /etc/network/interfaces:
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet manual
# For more iwpriv options see http://madwifi-project.org/wiki/UserDocs/iwpriv
pre-up iwpriv wlan0 authmode 2
pre-up iwpriv wlan0 wds 1
wireless-essid mynetwork
wireless-key s:mysecurekey
# For more options see "man bridge-utils-interfaces"
auto br0
iface br0 inet dhcp
bridge_ports eth1 wlan0
To setup WPA or WPA2 authentication you need to install hostapd. In particular, refer this configuration.
athk WiFi AP mode problem: After joining two interface into a bridge, DHCP packets do not go from wlan0 to eth1 interface, so the WiFi client cannot join the network.
What is “wmaster0”?
How to install Windows driver into Linux using NDISwrapper?
dmesg:
usb 1-1: new high-speed USB device number 2 using ehci_hcd usb 1-1: New USB device found, idVendor=0df6, idProduct=000d usb 1-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 usb 1-1: Product: RTL8187_Wireless_LAN_Adapter usb 1-1: Manufacturer: Manufacturer_Realtek_RTL8187_ usb 1-1: SerialNumber: 000CF63A630A
When you do this, you see in dmesg the following:
ndiswrapper version 1.57 loaded (smp=no, preempt=no) ndiswrapper: driver rtl8187a (Realtek Semiconductor Corp.,06/13/2008,5.1313.0613.2008) loaded wlan0: ethernet device 00:0c:f6:3a:63:0a using NDIS driver: rtl8187a, version: 0x1, NDIS version: 0x500, vendor: 'Realtek RTL8187 Wireless LAN USB NIC', 0DF6:000D.F.conf wlan0: encryption modes supported: WEP; TKIP with WPA, WPA2, WPA2-PSK; AES/CCMP with WPA, WPA2, WPA2-PSK usbcore: registered new interface driver ndiswrapper
and your wlan0 interface is ready to be configured in normal way.
ndiswrapper does not support master mode.
How to list all SSL ciphers?
openssl ciphers -v
or the same, but with filtering:
openssl ciphers -v 'HIGH:!SSLv2:!SSLv3:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!PSK:!MD5:@STRENGTH'
To list all ciphers that the service supports, use nmap ssl-enum-ciphers:
# nmap --script ssl-enum-ciphers -p 443 127.0.0.1 Starting Nmap 6.47 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2014-10-18 19:37 CEST Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1) Host is up (0.00013s latency). PORT STATE SERVICE 443/tcp open https | ssl-enum-ciphers: | SSLv3: No supported ciphers found | TLSv1.0: | ... | TLSv1.1: | ... | TLSv1.2: | ciphers: | TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA - strong | TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 - strong | TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 - strong | TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA - strong | TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 - strong | TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 - strong | TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA - strong | TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 - strong | TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 - strong | TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA - strong | TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 - strong | TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 - strong | compressors: | NULL |_ least strength: strong
To test if service supports given cipher, use:
openssl s_client -host localhost -port 993 -cipher 3DES
See also:
How to verify the fingerprint of the site?
# openssl x509 -in server.pem -fingerprint -noout [-sha256] SHA1 Fingerprint=30:46:D3:11:DC:8E:66:8B:36:8E:61:DB:DB:65:11:66:D8:6E:50:21
and on the client side it should result the same fingerprint:
# openssl s_client -connect host:443 | openssl x509 -fingerprint -noout depth=4 C = US, ST = UT, L = Salt Lake City, O = The USERTRUST Network, OU = http://www.usertrust.com, CN = UTN - DATACorp SGC verify error:num=19:self signed certificate in certificate chain verify return:0 SHA1 Fingerprint=30:46:D3:11:DC:8E:66:8B:36:8E:61:DB:DB:65:11:66:D8:6E:50:21
How to connect bluetooth keyboard
- Install
bluez:# apt-get install bluez
- Make sure that your bluetooth dongle is detected:
# dmesg Bluetooth: Core ver 2.16 Bluetooth: HCI device and connection manager initialized Bluetooth: HCI socket layer initialized Bluetooth: L2CAP socket layer initialized Bluetooth: SCO socket layer initialized Bluetooth: Generic Bluetooth USB driver ver 0.6 Bluetooth: RFCOMM TTY layer initialized Bluetooth: RFCOMM socket layer initialized Bluetooth: RFCOMM ver 1.11 Bluetooth: BNEP (Ethernet Emulation) ver 1.3 Bluetooth: BNEP filters: protocol multicast # lsusb Bus 003 Device 003: ID 0a12:0001 Cambridge Silicon Radio, Ltd Bluetooth Dongle (HCI mode) # hcitool dev Devices: hci0 00:1A:7D:DA:71:15 - Put the keyboard in discoverable mode and ensure you can see it
# hcitool scan Scanning ... 20:12:08:9A:18:20 Bluetooth keyboard for ipad - Pair with keyboard (
1234is entered and passed to keyboard where one should type it and press Enter) and connect to it:# bluez-simple-agent hci0 20:12:08:9A:18:20 RequestPinCode (/org/bluez/27229/hci0/dev_20_12_08_9A_18_20) Enter PIN Code: 1234 Release New device (/org/bluez/27229/hci0/dev_20_12_08_9A_18_20) # bluez-test-device trusted 20:12:08:9A:18:20 yes # bluez-test-input connect 20:12:08:9A:18:20
In bluez v5.23 and later the same should be performed using
bluetoothctl:# bluetoothctl [bluetooth]# pair 20:12:08:9A:18:20
- Verify the connection:
# hcitool con Connections: < ACL 20:12:08:9A:18:20 handle 71 state 1 lm MASTER AUTH ENCRYPT # dmesg Bluetooth: HIDP (Human Interface Emulation) ver 1.2 input: Bluetooth keyboard for ipad as /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1d.1/usb3/3-2/3-2:1.0/bluetooth/hci0/hci0:71/input13 generic-bluetooth 0005:05AC:023C.000C: input,hidraw1: BLUETOOTH HID v6.44 Keyboard [Bluetooth keyboard for ipad] on 00:1A:7D:DA:71:15 - In case the pairing should automatically happen during the boot, add the following:
rfcomm0 { bind yes; device 20:12:08:9A:18:20; comment "Bluetooth keyboard for ipad"; }In latest bluez versions the same should be performed using
bluetoothctl:# bluetoothctl [bluetooth]# trust 20:12:08:9A:18:20
- Remove the pairing:
# bluez-simple-agent hci0 20:12:08:9A:18:20 remove
In latest bluez versions the same should be performed using
bluetoothctl:# bluetoothctl [bluetooth]# remove 20:12:08:9A:18:20
See also:
Video
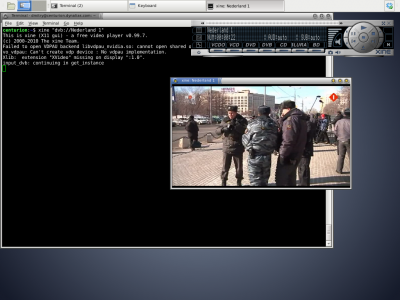
How to watch DVB-T TV channels?
- Buy module from DVB-T USB devices list. I have
DiBcom STK 7770Pthat comes with Dune HD. Make sure it is connected to PC:$ lsusb Bus 001 Device 002: ID 10b8:1e80 DiBcom
- Install
firmware-linux-nonfree. That will placedvb-usb-dib0700-1.20.fwinto/lib/firmware. Alternatively you can download it from here. - Reboot the system. This is required for firmware agent to load firmware needed by driver to the device.
usb 1-4: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 usb 1-4: Product: STK7770P_v1-4 usb 1-4: Manufacturer: DiBcom usb 1-4: SerialNumber: 005 dvb-usb: found a 'DiBcom STK7770P reference design' in cold state, will try to load a firmware usb 1-4: firmware: agent loaded dvb-usb-dib0700-1.20.fw into memory dvb-usb: found a 'DiBcom STK7770P reference design' in warm state. dvb-usb: will pass the complete MPEG2 transport stream to the software demuxer. dvb-usb: schedule remote query interval to 50 msecs. dvb-usb: DiBcom STK7770P reference design successfully initialized and connected. usbcore: registered new interface driver dvb_usb_dib0700
- Install
dvb-appsand perform the channel scanning:
scan /usr/share/dvb/dvb-t/nl-All > channels.conf
You will see among other staff something like this:>>> tune to: 722000000:INVERSION_AUTO:BANDWIDTH_8_MHZ:FEC_1_2:FEC_AUTO:QAM_64:TRANSMISSION_MODE_8K:GUARD_INTERVAL_1_4:HIERARCHY_NONE 0x0000 0x044d: pmt_pid 0x1b62 Digitenne -- Nederland 1 (running) 0x0000 0x044e: pmt_pid 0x1b6c Digitenne -- Nederland 2 (running) 0x0000 0x044f: pmt_pid 0x1b76 Digitenne -- Nederland 3 (running) 0x0000 0x0450: pmt_pid 0x1b80 Digitenne -- TV West (running) 0x0000 0x0457: pmt_pid 0x1bc6 Digitenne -- Radio West (running) 0x0000 0x0458: pmt_pid 0x1bd0 Digitenne -- Radio 1 (running) 0x0000 0x0459: pmt_pid 0x1bda Digitenne -- Radio 2 (running) 0x0000 0x045a: pmt_pid 0x1be4 Digitenne -- 3FM (running) 0x0000 0x045b: pmt_pid 0x1bee Digitenne -- Radio 4 (running) 0x0000 0x045c: pmt_pid 0x1bf8 Digitenne -- Radio 5 (running) 0x0000 0x045d: pmt_pid 0x1c02 Digitenne -- Radio 6 (running) 0x0000 0x045f: pmt_pid 0x1c16 Digitenne -- FunX (running) Network Name 'Digitenne'
- For e.g.
xineandmplayercopy the scanned channels information to~/.xine/channels.confand~/.mplayer/channels.confcorrespondingly. Launch the player:
xine "dvb://Nederland 1"
Other links on the topic:
How to setup DLNA server?
- Самосборный NAS на базе Mini-ATX Intel D425KT – скачивание торрентов, раздача контента по DLNA, постановка торрентов на закачку с iPad
djmount– mount MediaServers content as a Linux filesystem
How to setup OPDS server?
How to setup framebuffer?
# echo "options i915 modeset=1" > /etc/modprobe.d/framebuffer.conf
and then reboot (most of modules are compiled to kernel). Kernel messages:
# dmesg | egrep -i '(fb0|vesafb|inteldrmfb|i915|video|console)'
Console: colour dummy device 80x25
pci 0000:00:02.0: Video device with shadowed ROM at [mem 0x000c0000-0x000dffff]
vesafb: mode is 640x480x32, linelength=2560, pages=0
vesafb: scrolling: redraw
vesafb: Truecolor: size=8:8:8:8, shift=24:16:8:0
vesafb: framebuffer at 0xe0000000, mapped to 0x00000000e4f3f729, using 1216k, total 1216k
Console: switching to colour frame buffer device 80x30
fb0: VESA VGA frame buffer device
i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] PipeC fused off
i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] VT-d active for gfx access
fb0: switching to inteldrmfb from VESA VGA
Console: switching to colour dummy device 80x25
i915 0000:00:02.0: vgaarb: deactivate vga console
i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] DMAR active, disabling use of stolen memory
i915 0000:00:02.0: vgaarb: changed VGA decodes: olddecodes=io+mem,decodes=io+mem:owns=io+mem
[drm] Initialized i915 1.6.0 20200917 for 0000:00:02.0 on minor 0
ACPI: Video Device [GFX0] (multi-head: yes rom: no post: no)
input: Video Bus as /devices/LNXSYSTM:00/LNXSYBUS:00/PNP0A08:00/LNXVIDEO:00/input/input6
snd_hda_intel 0000:00:03.0: bound 0000:00:02.0 (ops i915_audio_component_bind_ops [i915])
i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] Cannot find any crtc or sizes
fbcon: i915drmfb (fb0) is primary device
Console: switching to colour frame buffer device 240x67
i915 0000:00:02.0: [drm] fb0: i915drmfb frame buffer device
# fbset
mode "1920x1080"
geometry 1920 1080 1920 1080 32
timings 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
accel true
rgba 8/16,8/8,8/0,0/0
endmode
See also:
X Window Server headless configuration: it is not possible to start X Server without any monitor physically attached to the PC?
Section "Device" Option "NoDDC" true Option "NoEDID" "1" Option "IgnoreEDID" true Driver "i810" EndSection
Interesting fonts on Debian
Xfce window manager crashes with segfault in libdbus-glib.so
$ xfce4-session Bus error $ xfce4-session Segmentation fault $ dmesg | grep xfce4 [Fri Dec 8 20:20:44 2017] xfce4-session[26591]: segfault at 0 ip b6b14900 sp bfbe6bdc error 6 in libdbus-glib-1.so.2.3.3[b6b07000+2a000]
apt-get install --reinstall xfce4-session libdbus-1-3 libdbus-glib-1-2 libglib2.0-0 libxfce4ui-1-0 libxfce4util7 libxfconf-0-2 xfce4-settings
Other relative issues:
Xfce sensors plugin starts with error that is cannot execute hddtemp
xcfe4-sensors-plugin is compiled without netcat feature, hence cannot read temperature information from socket. The solution suggested in documentation (/usr/share/doc/xfce4-sensors-plugin/README.Debian) is to set UID flag on hddtemp by running dpkg-reconfigure hddtemp.
Relevant links:
Installation of Plex media server
- Download package from site.
 After installing, edit the file
After installing, edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/plexmediaserver.listand uncomment repository location. This will allow to update Plex usingapt update && apt install plexmediaserver.- Open
http://1.2.3.4:32400/weband complete setup. - To setup SSL, follow LetsEncrypt HTTPs Plex guide. Mind that Custom certificate encryption key is a password.
 Check How Plex is doing HTTPS for all its users about how default HTTPs setup works.
Check How Plex is doing HTTPS for all its users about how default HTTPs setup works.
 If occasionally you have enabled required secure connections while not completing SSL setup (and have lost connection to the server), you can revert the setting by modifying the configuration file
If occasionally you have enabled required secure connections while not completing SSL setup (and have lost connection to the server), you can revert the setting by modifying the configuration file /var/lib/plexmediaserver/Library/Application Support/Plex Media Server/Preferences.xml and setting secureConnections=1 (check here for all options).
 Log files are located in
Log files are located in /var/lib/plexmediaserver/Library/Application Support/Plex Media Server/Logs.
See also:
Audio
How to save master sound level for ALSA?
/etc/init.d/alsa-utils). To do it manually, do the following:
alsactl –file /var/lib/alsa/asound.state store
How set a default sound card for ALSA?
- List cards via
aplay -L - Test card/devices using
$ for i in 3 7 8 9 10; do echo "[hw:0,$i]"; speaker-test -D hw:0,$i -l1 -c2; sleep 5s; done // Successful detection: Playback device is hw:0,7 Stream parameters are 48000Hz, S16_LE, 2 channels ... 0 - Front Left 1 - Front Right // Unsuccessful detection: Playback device is hw:0,8 Stream parameters are 48000Hz, S16_LE, 2 channels ... 0 - Unknown 1 - Unknown
- Create
~/.asoundrcor/etc/asound.conf:# cat <<EOF > /etc/asound.conf defaults.pcm.card 0 defaults.pcm.device 7 EOF
See also:
Devices and filesystems
- BindFS – user-space bind mount with possibility to alter permissions on-the-fly.
- Корневая файловая система Linux полностью на tmpfs – но обновления не записываются назад (нельзя доустановить или сохранить конфигурацию)
- Фикс падения производительности при копировании/закачке файлов в Linux – описание планировщиков ввода-вывода и их настройка
md-RAID
(sources (44 KiB, 912 downloads))
Bad block support:
A manual check can be triggered via:
echo check > /sys/block/mdX/md/sync_actioncheckarray -a /dev/mdX
Usually this operation is scheduled via cron (e.g. runs on first Sunday of each month). The status and progress can be checked as following:
# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid6] [raid5] [raid4] [raid1]
md0 : active raid1 sdb1[0] sdc1[1]
3906778112 blocks super 1.2 [2/2] [UU]
[>....................] check = 4.0% (158288320/3906778112) finish=386.5min speed=161604K/sec
bitmap: 0/30 pages [0KB], 65536KB chunk
The check operation scans the drives for bad sectors and automatically repairs them. If while reading, a read error occurs, the check will trigger the normal response to read errors which is to generate the “correct” data and try to write that out – so it is possible that a check will trigger a write. However in the absence of read errors it is read-only.
When the check is complete, one may check how many blocks (if any) have been flagged as bad (cat /sys/block/mdX/md/mismatch_cnt). mismatch_cnt is the number of unsynchronized blocks in the RAID.
echo repair >/sys/block/mdX/md/sync_action) which does not reset the count, but if you force a check after the rebuild is complete, then the count should return to zero.
 Unconfirmed that repair is needed on modern kernels.
Unconfirmed that repair is needed on modern kernels.
Kernel 3.1: Bad block management
Write error will not fail the drive but will record the location of the write error log. Kernel will use that bad block log to record failed blocks rather than failing the whole device. After a re-assembly (e.g. when you boot up after fixing your power, cable, controller issues) md will try writing to bad blocks again, until any such writes fail, after which it will stop trying to write to bad blocks on that device. By this method, md can automatically recover from spurious write failures caused by temporary issues.
Kernel 3.7: Support for TRIM operations for the underlying SSD
Btrfs
-
-
- Replacing a drive on a running RAID-5 array is not yet implemented in straightforward way (needs device deletion / rebalancing + addition).
- ZFS possesses similar features.
- According to FAQ it is strongly advised to use ×64 architecture.
Corruption detection and correction capabilities of btrfs
- From Know which HDDs fail beforehand:For example, we can see that maximal value taken by SMART attribute 197 over 30 days is a strong pre-failure signal. SMART 197 tracks current pending sector count. As long as value stays at 0, there is hardly no chance drive will fail over next day. But once value goes beyond 8, drive will certainly fail over next day with 88% chance. Focusing on top 4 hard drives with highest probability of failures, we would have achieved a precision rate of 46% when observing failure rate over 30 days.
- Can btrfs ignore bad blocks as they are discovered?
No, it is not keeping track of bad blocks. - If the drive does not successfully resolve the bad block issue and btrfs takes a write failure every time it attempts to overwrite the bad data, it is not going to remap that data, but rather it is going to fail the drive?If the drive doesn't resolve a bad block on write, then the drive is toast. That's how
mdhandles it. That's even how manufacturers handle it. The point at which write failures occur mean there are no reserve sectors left, or the head itself is having problems writing data to even good sectors. Either way, the drive isn't reliable for rw purposes and coming up with a bunch of code to fix bad drives isn't worth development time in my opinion. - How does btrfs handle bad blocks in RAID-1?If a block is read and fails its checksum, then the other copy (in RAID-1) is checked and used if it's good. The bad copy is overwritten with good data e.g.
BTRFS error (device sda1): fixed up error at logical 92686401536 on dev /dev/sdb1appears in kernel log. If the block is bad such that writing to it won't fix it (the drive returns an IO error) btrfs will complain in kernel log e.g.BTRFS error (device sda1): bdev /dev/sdb1 errs: wr 47, rd 0, flush 1, corrupt 0, gen 0. - Is running btrfs on top of LVM quite as efficient as btrfs by itself?LVM is like md RAID in that regard – no checksums, leaving the software entirely at the mercy of the hardware's ability to detect and properly report failure.
In fact, it's exactly as bad as that, since while both
lvmandmdoffer N-way-mirroring, they generally only fetch a single unchecksummed copy from whatever mirror they happen to choose to request it from, and use whatever they get without even a comparison against the other copies to see if they match or majority vote on which is the valid copy if something doesn't match. The only way they know there's an error (unless the hardware reports one) at all is if a deliberate scrub is done.And the RAID-5/6 parity-checking isn't any better, as while those parities are written, they're never checked or otherwise actually used except in recovery. Normal read operation is just like RAID-0; only the device(s) containing the data itself is(are) read, no parity/checksum checking at all, even the trouble was taken to calculate and write it out. When I had
mdRAID-6 deployed and realized that, I switched back to RAID-1 (which would have been RAID-10 on a larger system), because while I considered the RAID-6 performance costs worth it for parity checking, they most definitely weren't once I realized all those calculates and writes were for nothing unless an actual device died, and RAID-1 gave me that level of protection at far better performance.Btrfs will not return corrupted data unless CoW is disabled (noCoW turns of checksumming only for data, i.e. metadata is always checksummed). However btrfs will also not repair the “bad” copy – use
btrfs scrubfor that. - CoW, checksumming and consistencyIf the file is CoW'd and checksummed, and there's a crash, there is supposed to be consistency: either the old state or new state for the data is on-disk and the current valid metadata correctly describes which state that data is in.
If the file is not CoW'd and not checksummed, its consistency is unknown but also ignored when doing normal reads, balance or scrubs.
If the file is not CoW'd but were checksummed, there would always be some inconsistency if the file is actively being modified. Only when it's not being modified, and metadata writes for that file are committed to disk and the superblock updated, is there consistency. At any other time, there's inconsistency. So if there's a crash, a balance or scrub or normal read will say the file is corrupt. And the normal way Btrfs deals with corruption on reads from a mounted fs is to complain and it does not pass the corrupt data to user space, instead there's an i/o error. You have to use restore to scrape it off the volume; or alternatively use btrfsck to recompute checksums.
- RAID-Z and dynamic stripe widthRAID-5 (and other data/parity schemes such as RAID-4, RAID-6, even-odd, and Row Diagonal Parity) never quite delivered on the RAID promise – and can't – due to a fatal flaw known as the RAID-5 write hole. Whenever you update the data in a RAID stripe you must also update the parity, so that all disks XOR to zero – it's that equation that allows you to reconstruct data when a disk fails. The problem is that there's no way to update two or more disks atomically, so RAID stripes can become damaged during a crash or power outage.
To see this, suppose you lose power after writing a data block but before writing the corresponding parity block. Now the data and parity for that stripe are inconsistent, and they'll remain inconsistent forever (unless you happen to overwrite the old data with a full-stripe write at some point). Therefore, if a disk fails, the RAID reconstruction process will generate garbage the next time you read any block on that stripe. What's worse, it will do so silently – it has no idea that it's giving you corrupt data.
There's also a nasty performance problem with existing RAID schemes. When you do a partial-stripe write – that is, when you update less data than a single RAID stripe contains – the RAID system must read the old data and parity in order to compute the new parity. That's a huge performance hit. Where a full-stripe write can simply issue all the writes asynchronously, a partial-stripe write must do synchronous reads before it can even start the writes.
btrfs on flash/USB devices
- btrfs on flash/USB devices:CoW designs tend naturally to work well with flash media. F2FS is specifically designed to work well with flash, whereas for btrfs it is a natural consequence of the copy-on-write design. With both filesystems, if you randomly generate a 1GB file and delete it 1000 times, onto a 1TB flash, you are very likely to get exactly one write to every block on the flash (possibly two writes to <1% of the blocks) rather than, as would be the case with non-CoW filesystems like FAT, 1000 writes to a small chunk of blocks.
- USB drives:There's several possibilities for failure, including flaky connections (sometimes assisted by cats or kids), unstable USB host port drivers, and unstable USB/ATA translators. A number of folks have reported problems with such filesystems with devices connected over USB, that simply disappear if they direct-connect the exact same devices to a proper SATA port. The problem seems to be /dramatically/ worse with USB connected devices, than it is with, for instance, PCIe-based SATA expansion cards.
Replacing failing device
So in summary, without temporarily adding an additional drive, there are 3 ways to replace a drive (see Replacing drives with larger ones in a 4 drive raid1):
- Logically removing old drive (triggers 1st rebalance), physically removing it, then adding new drive physically and logically (triggers 2nd rebalance).
- Physically removing old drive, mounting degraded, logically removing it (triggers 1st rebalance, while degraded), then adding new drive physically and logically (2nd rebalance).
- Physically replacing old with new drive, mounting degraded, then logically replacing old with new drive (triggers rebalance while degraded).
Shrink btrfs partition
btrfs dev resize to shrink it to (slightly smaller than) the replacement device, then btrfs replace should work. Then btrfs dev resize max to fill up the replacement device completely.
How to convert RAID1 volume into single-drive volume
/dev/sdb is failing drive which we want to remove, and remaining /dev/sda should be converted into single-drive volume:- Detach failing drive or run
echo 1 > /sys/block/sdb/device/delete(check here for more information) - Mount healthy device in degraded mode:
mount /dev/sda /mnt/tmp -o degraded - Convert from RAID1 to RAID0:
btrfs balance start -f -mconvert=single -dconvert=single /mnt/tmp - Remove detached drive from btrfs volume:
btrfs device remove missing /mnt/tmp
btrfs device delete /dev/sdc1 /mnt/raid1 user experience
-o degraded and you can re-establish two copy replication with btrfs dev add with a new drive and btrfs dev del missing to get rid of the phantom missing drive.
A gotcha with this technique though is often single chunks get created during the -o degraded read-write mount. After dev del missing completes the replication process, you need to check btrfs fi df or btrfs fi us for single chunks. If they exist, get rid of them with a filtered balance: btrfs balance -dconvert=raid1,soft -mconvert=raid1,soft should work I think. If there are single chunks created and not converted, later if you need to do a degraded mount it will fail. Usually it can be made to work with -o ro,degraded in such a case, but it means no more read-write for the file system and you'd have to recreate it.
btrfs corruption when devices are missing for kernels before 4.3
btrfs device delete (some stripes will be missing). The situation is even worse if RAID0 is used for the the metadata: trying to mount a BTRFS volume in read/write mode while not all the devices are accessible will simply kill the remaining metadata, hence making the BTRFS volume totally unusable… you have been warned!
 This is not actually true, but the bug is better explained here and there:
This is not actually true, but the bug is better explained here and there:
Loss of one device of a two-device raid1 (in case mounting degraded writable) will force new chunks to be written in single mode, because there's not a second device to write to (so writing raid1 is no longer possible). So far, so good. But then on an unmount and attempt to mount again, btrfs sees single mode chunks on a two-device btrfs, and knows that single mode normally won't allow a missing device, so forces read-only, thus blocking adding a new device and rebalancing all the single chunks back to raid1. The fix will be in first Linux kernel 4.3 release.
btrfs corruption due to partition cloning / UUID collision
If you clone a filesystem (for instance using dd or lvm snapshotting, doesn't matter how) and then trigger a btrfs device scan, say by plugging in some other device with btrfs on it so udev triggers a scan, and the kernel sees multiple devices with the same filesystem UUID as a result, and one of those happens to be mounted, you can corrupt both copies as the kernel btrfs won't be able to tell them apart and may write updates to the wrong one.
Prevention: Don't let btrfs see both copies at the same time. If you need to clone the filesystem, ideally make sure it's unmounted at the time, and detach either the original device or the clone immediately upon finishing the clone operation (before doing anything that might trigger a btrfs device scan, including device plugging that would trigger udev to trigger such a scan). Then simply keep them separate, only attaching one at a time and definitely never mounting the filesystem with both the clone and the original devices attached, so the kernel can't get confused and write to the wrong one because the other one is never there at the same time to provide the opportunity.
Cannot balance FS (No space left on device)
balance -dlimit=20, it doesn't pack that all into the first chunk, it allocates a new chunk, and then packs it all into that, then frees all the other chunks. This behaviour is actually a pretty important property when adding or removing devices or converting between profiles, because it's what forces things into the new configuration of the filesystem.
In an ideal situation, the limit filters should make it repack into existing chunks when specified alone, but currently that's not how it works, and I kind of doubt that that will ever be how it works.
Allocation policy
If you're using a striped RAID level (0, 5, 6), then btrfs will fill up the devices equally, until one is full, and then switch to using the remaining devices (until one is full, etc).
Data read load balancing
defrag after dedup
Defrag before dedup is a more complex situation that depends on the dedup strategy of whichever dedup tool you are using:
- A file-based dedup tool doesn't have to care about extent boundaries, so you can just run defrag and then dedup – in that order.
- An extent-based dedup tool will become less efficient after defrag and some capabilities will be lost, e.g. it will not be able to dedup data between VM image files or other files on the host filesystem. Extents with identical content but different boundaries cannot be deduped. There are fewer opportunities to find duplicate extents because defrag combines smaller extents into bigger ones.
- A block-based dedup tool explicitly arranges the data into extents by content, so extents become entirely duplicate or entirely unique. This is different from what defrag does. If both are run on the same data they will disagree on physical data layout and constantly undo each other's work.
When data is defragged, it appears in find-new output as “new” data (the same as if the data had been written to a file the usual way). An incremental dedup tool that integrates defrag and find-new at the same time has to carefully prevent itself from consuming its own output in an endless feedback loop.
shapshots influence on defrag
btrfs zone types
From here:
- Unallocated (unzoned)
Can be used for anything but must be allocated/zoned first - System
Critical but limited in size and generally only allocated at mkfs or when adding a new device. - Data
The actual file storage, generally the largest allocation. - Metadata
Information about the files: where they are located (the location and size of individual extents), ownership and permissions, date stamps, checksums, and for very small files (a few KiB), sometimes the file content itself.- Global reserve
A small part of metadata reserved for emergency use only. Btrfs is pretty strict about its use, and will generally error out withENOSPCif metadata space other than the global reserve is used up, before actually using this global reserve. As a result, any of the global reserve used at all indicates a filesystem in very severe straits, crisis mode.
Btrfs in practice tends to be a bit liberal about allocating/zoning data chunks, since it's easier to find bigger blocks of space in unallocated space than it is in busy partly used data space. Over time, therefore, more and more space tends to be allocated to data, while existing data space, like those blocks near city center, may have most of its files/buildings deleted, but still have a couple still occupied.
From here:
-d and -m filters exactly duplicate each other (balance -dusage=50 -musage=50). Otherwise invoking balance with both an -musage and a -dusage filter is rare except the examples dealing with specific cases where metadata or data (usually metadata), has run out, due to the other one (data), taking all the unallocated space with mostly empty allocations. So a quick -dusage filter to clear out the mostly empty data allocations is the most common example seen.
How to map btrfs logical sector to physical sector?
[17606.989497] BTRFS error (device sdb1): unable to fixup (regular) error at logical 3037444042752 on dev /dev/sdc1
# btrfs-map-logical -l 3037444042752 /dev/sdc1 mirror 1 logical 3037444042752 physical 2554240299008 device /dev/sdc1 ... # dd if=/dev/sdc1 bs=4096 skip=2554240299008 count=1 of=block_sdc1
Is there a way to map inodes to paths?
btrfs inspect-internal inode-resolve <inode> <volume>
This resolves the <inode> in subvol <volume> to its fs paths
I've got some bad blocks on partition. How can I fix it?
kernel: sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Unhandled sense code kernel: sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Result: hostbyte=DID_OK driverbyte=DRIVER_SENSE kernel: sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Sense Key : Medium Error [current] [descriptor] kernel: Descriptor sense data with sense descriptors (in hex): kernel: 72 03 11 04 00 00 00 0c 00 0a 80 00 00 00 00 00 kernel: 01 58 f6 f9 kernel: sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] Add. Sense: Unrecovered read error - auto reallocate failed kernel: sd 2:0:0:0: [sda] CDB: Read(10): 28 00 01 58 f6 f8 00 00 08 00
and smartd daemon reports:
Device: /dev/sda [SAT], 1 Currently unreadable (pending) sectors
The legal approach is to dump the whole FS somewhere, run badblocks8) utility on the given partition and reformat it (will work for e.g. EXT3). Unfortunately, mkfs.xfs (and mkfs.reiserfs) does not take any list of bad blocks which can be fed from badblocks and XSF does not support list of bad blocks as well.
First what you can try, is to read all files from filesystem (e.g. tar -c / -O > /dev/null or find / -type f -exec cp '{}' /dev/null \; or genisoimage -D -r -udf -allow-limited-size / > /dev/null) and see what files are failed to read. Then you need to nullify this file, e.g. via dd if=/dev/zero of=/bad/file bs=1 count=<file_size>. If the faulty file was not found then follow the steps described in Bad block HOWTO. In two words: you need to find out the number of the block (using e.g. dd) that fails, move (or remove) the file that contains this block, to different place and nullify the block. After that HDD will notice that block is ready for re-allocation and replacement with another block from a pool for such cases.
Another solution could be to create partitions so that bad blocks do not belong to partitioned areas (see Как удалось оживить битый HDD для хранения чего-нибудь ненужного) and join them using mdadm or LVM or btrfs.
Additional links:
Ext4-fs reports corruption problems
EXT4-fs error (device sda3): ext4_ext_check_inode:481: inode #4857903: comm updatedb.mlocat: pblk 0 bad header/extent: too large eh_max - magic f30a, entries 1, max 1540(4), depth 0(0) EXT4-fs error (device sda3): ext4_ext_check_inode:481: inode #4724129: comm tar: pblk 0 bad header/extent: invalid extent entries - magic f30a, entries 1, max 4(4), depth 1(1) EXT4-fs error (device sda4): ext4_mb_generate_buddy:756: group 162, 27838 clusters in bitmap, 27848 in gd; block bitmap corrupt. EXT4-fs (sda4): Inode 1574118 (ede4e380): orphan list check failed! EXT4-fs error (device sda2): htree_dirblock_to_tree:920: inode #264418: block 1057309: comm find: bad entry in directory: rec_len % 4 != 0 - offset=524(524), inode=18087964, rec_len=28781, name_len=116 EXT4-fs (sda2): Remounting filesystem read-only
After some time, partition(s) are re-mounted read-only and system operation shortly stops.
Common cause of this is the block address getting corrupted, so that the hard drive read the correct data from the wrong location.
but it turned out to be the problem with one of the memory bank which was corrupting the data (and by co-incidence allocated for disk buffers). As overview:
- If problem occurs on different partitions or drives but S.M.A.R.T. indicators are not going worth, then it is a signal that problem is not connected with hard drive damage.
- If filesystem repair is started (e.g.
fsck /dev/sda2), it reports about corrupted directory entries, orphan free blocks (and so on), it fixes the problems and you immediately re-runfsckand it finds the same sort of problems again, then the corruption happens either when data is transferred to hard drive or back from it.
… it's time to run memtest which will anyway not harm, but will save you many hours trying to find a problem in hard drive or cables or controller.
How to force OS to check given filesystem on startup?
fsck.mode=force to kernel parameters (for example, edit /etc/default/grub, modify GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT and run update-grub).  Use
Use fsck.repair=preen to automatically fix what can be safely fixed.
See also Fsck in relation to how tune ext2/3/4 filesystems to be checked after certain amount of time or mounts.
 How to force OS to check given filesystem on startup?:
How to force OS to check given filesystem on startup?:
- Run
touch forcefsckin the root directory of the mounted filesystem. This file will be removed after filesystem is checked at boot. - Add
forcefsckto kernel options. This will force check for all filesystems to be mounted at boot.
How to mount XFS filesystem with extended file attributes support?
How to use video RAM as block device
Unlike motherboard RAM and hard drives, there aren't any known video cards that have ECC memory. This may not be a big deal for graphics rendering, but you definitely don't want to put critical data in it or use this feature on servers.
Example of allocating 123MB (0x7b00000) vRAM with 1280×1024 32bit display (check fbset output):
# lspci -vvv | less
01:05.0 VGA compatible controller [0300]: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] RS690M [Radeon Xpress 1200/1250/1270] [1002:791f] (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
Subsystem: Toshiba America Info Systems RS690M [Radeon Xpress 1200/1250/1270] [1179:ff1a]
Control: I/O+ Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx-
Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-
Latency: 64, Cache Line Size: 32 bytes
Interrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 18
NUMA node: 0
Region 0: Memory at f0000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=128M]
Region 2: Memory at f8100000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=64K]
Region 4: I/O ports at 9000 [size=256]
Region 5: Memory at f8000000 (32-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=1M]
[virtual] Expansion ROM at 000c0000 [disabled] [size=128K]
Capabilities: [50] Power Management version 2
Flags: PMEClk- DSI- D1+ D2+ AuxCurrent=0mA PME(D0-,D1-,D2-,D3hot-,D3cold-)
Status: D0 NoSoftRst- PME-Enable- DSel=0 DScale=0 PME-
Capabilities: [80] MSI: Enable- Count=1/1 Maskable- 64bit+
Address: 0000000000000000 Data: 0000
Kernel driver in use: radeon
Kernel modules: radeon
# modprobe slram map=VRAM,0xf0500000,+0x7b00000 # 1280*1024*4 = 0x500000 → 0xf0500000,+0x7b00000
# modprobe mtdblock
# hdparm -t /dev/mtdblock0
/dev/mtdblock0:
Timing buffered disk reads: 48 MB in 3.10 seconds = 15.49 MB/sec
Using compressed in-memory drives
 One can install
One can install zram-tools (which installs zramswap.service) and modify /etc/default/zramswap as needed, however unfortunately this package only focuses on swap, i.e. it is cumbersome to tune other zram partitions for other needs.
More flexible is the following approach:
- Enable
zrammodule and tune it for 2 devices:# cat > /etc/modules-load.d/zram-drive.conf <<'EOF' zram EOF # cat > /etc/modprobe.d/zram-drive.conf <<'EOF' options zram num_devices=2 EOF
- Run
modprobe zramand check that devices have been created:# ls -l /dev/zram* brw-rw---- 1 root disk 254, 0 Dec 29 22:56 /dev/zram0 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 254, 1 Dec 29 22:56 /dev/zram1
- Make use of
zram-setup@.servicefromudisks2package. This service reads settings from/usr/local/lib/zram.conf.d/%i-envby default (where%iis substituted by device name e.g.zram0) but it can be tuned as following:# cat > /etc/systemd/system/zram-setup@.service <<'EOF' # # Service initializes zram devices # [Unit] Description=Setup zram based device %i Requires=dev-%i.device After=dev-%i.device Before=local-fs.target [Service] Type=oneshot RemainAfterExit=yes EnvironmentFile=-/etc/zram.conf.d/%i ExecStart=/bin/sh -c 'if [ -n "$ZRAM_COMPRESSION" ]; then echo $ZRAM_COMPRESSION > /sys/class/block/%i/comp_algorithm; fi' ExecStart=/bin/sh -c 'if [ -n "$ZRAM_STREAMS_NUM" ]; then echo $ZRAM_STREAMS_NUM > /sys/class/block/%i/max_comp_streams; fi' ExecStart=/bin/sh -c 'if [ -n "$ZRAM_DEV_SIZE" ]; then echo $ZRAM_DEV_SIZE > /sys/class/block/%i/disksize; fi' ExecStart=/bin/sh -c 'if [ "$SWAP" = "y" ]; then mkswap /dev/%i && swapon /dev/%i; fi' ExecStart=/bin/sh -c 'if [ "$MKE2FS" = "y" ]; then mke2fs -q -m 0 -b 4096 -O sparse_super -L %i /dev/%i && mount -t ext2 /dev/%i /tmp && chmod 1777 /tmp; fi' ExecStop=-/bin/sh -c 'echo 1 > /sys/class/block/%i/reset' [Install] WantedBy=local-fs.target EOF # cat > /etc/zram.conf.d/zram0 <<'EOF' ZRAM_COMPRESSION=lz4 ZRAM_DEV_SIZE=100M SWAP=y EOF # cat > /etc/zram.conf.d/zram1 <<'EOF' ZRAM_COMPRESSION=lz4 ZRAM_DEV_SIZE=100M MKE2FS=y EOF # systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl enable zram-setup@zram0.service # systemctl enable zram-setup@zram1.service
- Make sure that swap partition is active and /tmp is mounted:
# swapon NAME TYPE SIZE USED PRIO /dev/zram0 partition 100M 100M -2 # systemctl status tmp.mount * tmp.mount - /tmp Loaded: loaded Active: active (mounted) since Sat 2020-10-03 01:44:10 CEST; 3 months 4 days ago Where: /tmp What: /dev/zram1 Tasks: 0 (limit: 4915) Memory: 0B CGroup: /system.slice/tmp.mount
 In above approach there is a need to mount
In above approach there is a need to mount /tmp just because it should be set 1777 permission afterwards. Unfortunately there is no “mode=1777” mount option for ext2 (as for tmpfs) otherwise it would be possible to leverage mounting step to /etc/fatab.
See also:
Renaming a file on Samba share does not always correspond to Linux ideology
map readonly = no map archive = no map system = no map hidden = no
Another possible variants is to use store dos attributes = yes and delete readonly = yes.
Map Windows user to Unix user
- Create new TDB using
tdbtool dummy.tdb create /var/lib/samba/winbindd_idmap.tdb - Add
idmap config * : tdbto/etc/samba/smb.conf
To get list of cashed SID↔UID mappings:
# net cache list | grep S-1-5-21 Key: IDMAP/SID2XID/S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3000 Timeout: Sun Jul 22 20:53:17 2010 Value: 1000:U Key: IDMAP/UID2SID/1000 Timeout: Sun Jul 22 20:53:17 2010 Value: S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3000 Key: IDMAP/SID2XID/S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-501 Timeout: Sun Jul 22 23:17:17 2010 Value: 65534:U Key: IDMAP/UID2SID/65534 Timeout: Sun Jul 22 23:17:17 2010 Value: S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-501
To get local SID:
# net getlocalsid SID for domain HOMENET is: S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913
To list all Samba users (either from smbpasswd or LDAP – specified by passdb backend option in smb.conf):
# pdbedit -L -v Unix username: backup NT username: backup Account Flags: [U ] User SID: S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3000 Primary Group SID: S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-513 Full Name: Backup User Home Directory: \\homenet\backup HomeDir Drive: Logon Script: Profile Path: \\homenet\backup\profile Domain: HOMENET Account desc: Workstations: Munged dial: Logon time: 0 Logoff time: never Kickoff time: never Password last set: Sun, 12 Jul 2015 12:58:25 CEST Password can change: Sun, 12 Jul 2015 12:58:25 CEST Password must change: never Last bad password : 0 Bad password count : 0 Logon hours : FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
To change SID for the given user:
# pdbedit --user backup -U S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3001 smbldap_search_domain_info: Searching for:[(&(objectClass=sambaDomain)(sambaDomainName=HOMENET))] smbldap_open_connection: connection opened init_sam_from_ldap: Entry found for user: backup init_ldap_from_sam: Setting entry for user: backup ldapsam_update_sam_account: successfully modified uid = backup in the LDAP database
To get user→SID mapping from winbind (either from Samba user DB or as specified by idmap config option in smb.conf):
$ wbinfo -n '\backup' S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3000 SID_USER (1)
To get SID→user mapping from winbind:
$ wbinfo --lookup-sids S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3000 S-1-5-21-2724446181-3664060749-2626026913-3000 -> <none>\backup 1
To get user→SID mapping on Windows:
C:\> wmic useraccount get name,sid Name SID Administrator S-1-5-21-1827375663-6890924511-1272660413-500 User S-1-5-21-1827375663-6890924511-1272660413-1000
See also:
How to list the content of remote share?
smbclient //server/share -c ls
How to configure HDD to spin-off after certain inactivity time?
/etc/hdparm.conf. The options from that section are applied to corresponding drive once it is attached to the system:
/dev/disk/by-uuid/91e32677-0656-45b8-bcf5-14acce39d9c2 {
spindown_time = 240
}
How to mark USB flash as non-rotating device?
/dev/disk/by-id directory or lsusb output./etc/udev/rules.d/90-non-rotational.rules
# Mark given USB devices as non-rotational:
ACTION=="add|change", SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", ENV{ID_SERIAL}=="SanDisk_Ultra_Fit_*-0:0", ATTR{queue/rotational}="0", ATTR{queue/scheduler}="deadline"
# Change scheduler for SSD drives:
ACTION=="add|change", KERNEL=="sd[a-z]", ATTR{queue/rotational}=="0", ATTR{queue/scheduler}="deadline"
To list all properties of the given drive use udevadm info -q all -n /dev/sda.
See also SSD optimization.
USB device is reporting usb 1-2: reset high speed USB device using ehci_hcd and address 2
- Check/change the USB cable
- Try another USB port
- Try to reduce the number of sectors to read/write to device (see Linux USB FAQ):
echo 16 > /sys/block/sdb/device/max_sectors - Disable
ehci_hcdmodule (this will downgrade USB from 2.0 to 1.1 thus reduce disk performance in times):
echo "blacklist ehci_hcd" >> /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
Further reading:
Posted by me:
What would be the performance impact if module uhci_hcd is used instead of ehci_hcd?
# hdparm -tT /dev/sdb /dev/sdb: Timing cached reads: 2464 MB in 2.00 seconds = 1232.46 MB/sec Timing buffered disk reads: 92 MB in 3.04 seconds = 30.27 MB/sec # rmmod ehci_hcd [ 72.848048] ehci_hcd 0000:00:1d.7: USB bus 1 deregistered [ 72.850412] ehci_hcd 0000:00:1d.7: PCI INT A disabled [ 73.084041] usb 2-1: new full-speed USB device number 2 using uhci_hcd [ 73.332925] usb 2-1: New USB device found, idVendor=1058, idProduct=1104 [ 73.335280] usb 2-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=3 [ 73.337638] usb 2-1: Product: My Book [ 73.339936] usb 2-1: Manufacturer: Western Digital [ 73.342251] usb 2-1: SerialNumber: 575532553130303530353538 [ 73.397554] scsi5 : usb-storage 2-1:1.0 [ 73.479146] input: Western Digital My Book as /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1d.0/usb2/2-1/2-1:1.1/input/input4 [ 73.482549] generic-usb 0003:1058:1104.0002: input,hidraw0: USB HID v1.11 Device [Western Digital My Book] on usb-0000:00: # hdparm -tT /dev/sdb /dev/sdb: Timing cached reads: 2 MB in 2.01 seconds = 1016.81 kB/sec Timing buffered disk reads: 4 MB in 4.05 seconds = 1011.35 kB/sec
uhci_hcdis USB Universal Host Controller Interface driverehci_hcdis USB 2.0 'Enhanced' Host Controller (EHCI) driverxhci_hcdis USB 3.0 eXtensible Host Controller Interface (xHCI) driver
To check what module is used to access a specific, examine lsusb -tv output:
# lsusb -t
/: Bus 05.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=ehci-pci/8p, 480M
|__ Port 1: Dev 2, If 0, Class=Mass Storage, Driver=usb-storage, 480M
|__ Port 4: Dev 4, If 0, Class=Mass Storage, Driver=usb-storage, 480M
/: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=uhci_hcd/2p, 12M
|__ Port 2: Dev 2, If 0, Class=Hub, Driver=hub/4p, 12M
|__ Port 1: Dev 6, If 0, Class=Mass Storage, Driver=usb-storage, 12M
One can see that two first USB drives are connected via hi-speed interface, and third one via low-speed hub.
See also:
How to find all hard links?
find . -type f -links +1 -exec ls -li '{}' \;
After one can use one of the strategies to list particular group of files (from List all files with the same inode?):
find -samefile /some/filefind -inum 12353538
How to synchronize remote file contents with local one?
rsync -itmz -P --checksum --inplace -e 'ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null' file.7z host:/path/file.7z
To synchronize local folder with another local folder:
rsync -r --size-only Documents/ /cygdrive/d/Documents/ | grep -E '^(>|\*)'
How to optimize ISO image, making files with same content point to same data?
mkisofs-md5-2.01-xxx). However cdrtools-2.01.01.a59 and earlier do not compile under Debian 6.0, see this mail thread.
The patch cdrtools-3.00-duplicates-once-with-md5c.diff.bz2 (cdrtools-3.00-duplicates-once-with-md5c.diff.bz2.asc) includes the changes necessary to be applied on the top of original source to enable support of “duplicates-once” functionality. Compile the project with make. Use like this:
mkisofs -udf -iso-level 3 -duplicates-once -o /path/to/file.iso /path/to/data
Also posted here.
How to create DVD ISO from VIDEO_TS directory?
VIDEO_TS and AUDIO_TS, the following command will create DVD ISO:
genisoimage -dvd-video -V “My disk label” -o dvdimage.iso .
SuSE
Questions answered
How to list all packages installed during the given year?
$ rpm -qa --queryformat "%{NAME}\t%{DISTRIBUTION}\t%{INSTALLTIME:date}\n" | grep "2014$" | sort
libxfce4mcs openSUSE 11.1 Mon Jan 13 15:56:56 2014
libxfce4util openSUSE 11.1 Mon Jan 13 15:56:55 2014
libxfcegui4 openSUSE 11.1 Mon Jan 13 15:56:56 2014
Debian
How to configure proxy for APT?
echo 'Acquire::http::Proxy "http://centurion:3128";' > /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/99proxy
How to disable installation of recommended packages by default?
# cat > /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/01norecommend <<'EOF' APT::Install-Recommends "0"; APT::Install-Suggests "0"; EOF
After that if you want to override the behaviour use the following:
apt-get install --install-recommends ...
How to become a Debian Maintainer
- Debian New Maintainer page describes, who is Debian Maintainer, Debian Developer and Debian Sponsor.
- mentors – service to upload the packages to Debian via sponsor.
- The Debian-mentors FAQ provides step-by step manual for those who want to create a package.
- Howto create a Debian package – includes also recommendations and checklists from Debian developers and referred from above FAQ.
- AutoTools introduction – very nice
- Keysigning page describes how to get your PGP key signed (follow closest members in NL). You need it to upload the packages and communicate to other developers.
- Checklists for package maintainers, composed by some Debian sponsors:
Packaging hints
- Install the package sources using
apt-get source <package>. - Check if the package lintian clean (
lintian -i -I --show-overrides binpackage-version.deboutput fromlintianpackage). Check the description of the problem here (click on corresponding message reported). - Check if licenses are compatible across all sources (use
licensecheck -r .fromdevscriptspackage to display all of them). - Test all the .deb packages with
piuparts binpackage-version.deb(frompiupartspackage). - To find out what packages your package needs to be built run the command
dpkg-depcheck -d ./configure, to manually find exact build dependency for/usr/bin/fooexecuteobjdump -p /usr/bin/foo | grep NEEDED. - You need to specify the following in your
~/.profile:# For dh_make: export DEBEMAIL=joy-mg@debian.org DEBFULLNAME="Josip Rodin" # For debuild: export DEBUILD_LINTIAN_OPTS="-i -I --show-overrides" # For debsign: export DEBSIGN_KEYID="0x124AB157"
- To generate a stub
debiandirectory rundh_make --copyright gpl2(from packagedh_make). dchis used to add new entries to the changelog or modify existing ones:debchange --newversion X.Yto add new entrydebchange -a "New version 3.0" --closes 123,456to append to top-most entry
- To manipulate the patches use
quiltutility:quilt import -P local_file.patch external_file.patch
- … or dpatch utility:
cat my.patch | dpatch patch-template -p "nnn_short_description" "Some human friendly description." > nnn_file.dpatch; echo "nnn_file.dpatch" >> 00list
- To install all build dependencies use
apt-get build-dep <package>(if package is not installed / prepared) or
mk-build-deps -iif package is already downloaded and prepared viadpkg-source -x package.dsc. - The preferable way to build a project is
debuild -sa(it will rundpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot,lintiananddebsign) or
dpkg-buildpackage -b -rfakeroot -us -ucif source was not downloaded. - To clean the source tree run
make -f debian/rules cleanordebuild – cleanwhile will run the same command. - To list the contents of DEB file use
dpkg --contents filename.deb, and to print the specific file usedpkg --fsys-tarfile filename.deb | tar -xOf - --wildcards \*/copyright | less - You can run the
uscancommand fromdevscriptsto check for upstream updates based ondebian/watchfile. - To upload the package use
dupload -t mentors cream_1.23-1_i386.changes - To populate the documentation of the package to system-wide infrastructure have a look at
doc-baseproject. - To modify the
.debpackage usedpkg-deb -R original.deb tmp; vi tmp/DEBIAN/control; dpkg-deb -b tmp fixed.deb;
Questions answered
What are /usr/lib/pkgconfig/nnn.pc files?
pkg-config file contains the information about the package version, CFLAGS and LIBS used to assemble the package. It is preferred to libtool, and .la files are in the process of being replaced by .pc files.
Additional links:
- Guide to pkg-config by Dan Nicholson
debuild fails with missing file
/path/to/missing: no such file or directory
autoreconf -vif
apt-get update fails with signature verification error
apt-get update fails with the following error:
W: A error occurred during the signature verification. The repository is not updated and the previous index files will be used. GPG error: http://ftp.nl.debian.org sid InRelease: The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY 8B48AD6246925553 W: Failed to fetch http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/sid/InRelease
archive-key-7.0.asc is actually the latest one):wget -q http://ftp-master.debian.org/keys/archive-key-7.0.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
See also Force update from unsigned repository.
apt-get update fails with The method driver /usr/lib/apt/methods/http could not be found
apt-get install apt-transport-https
apt-get update fails with E: Repository '…' changed its 'Origin' value from '…' to '…'
Do apt-get update –allow-releaseinfo-change
How to reinstall already installed package?
apt-get install --reinstall package1 ...
How to mark manually installed package as 'auto'?
apt-mark:
# apt-get install libphp-adodb libphp-adodb is already the newest version (5.20.4-1). libphp-adodb set to manually installed. # apt-mark auto libphp-adodb libphp-adodb was set to automatically installed.
How to install a particular version of the package via apt-get (downgrade)?
apt-get install wine=1.6.2-20 wine32=1.6.2-20 libwine=1.6.2-20
After that it is advised to prevent auto updating the package to the newer version:
for package in wine wine32 libwine; do echo "$package hold" | dpkg --set-selections; done

apt-mark hold $package
Remind yourself which packages are on hold:
dpkg --get-selections | egrep 'hold$'

apt-mark showhold
To unhold the package run:
echo "$package unhold" | dpkg --set-selections

apt-mark unhold $package
More radically one can uninstall packages with dpkg -r --force-depends ... and install them from DEB.
How to install some local DEB package with dependencies from repository?
- Download DEB file(s) (if necessary) e.g. via
apt-get download my.deb  Install it via
Install it via dpkg -i my.deband install all dependencies viaapt-get install -f Install it via
Install it via apt-get install my.deb
How to output Debian dependency tree to terminal?
apt-rdepends-tree.sh outputs dependencies up to 2nd level.
How to ignore the post-install scripts for DEB package?
postinst file:
rm /var/lib/dpkg/info/<package>.postinst
How to list packages by installation date?
ls -lt /var/lib/dpkg/info/ | grep .list
How to verify files from installed packages?
debsums and run debsums -ca.
How to find out half-configured/broken packages?
dpkg-query -f '${status} ${package}\n' -W | grep “half-configured” or dpkg –audit.
How to recompile Debian kernel?
- Download & unpack kernel:
$ apt-get source linux-image-3.2.0-4-686-pae; cd linux-3.2.35
or if you have all prerequisites downloaded:
$ dpkg-source -x linux_3.2.41-4.dsc; cd linux-3.2.35 - [obsolete] Modify
debian/config/definesso that ABI is different. Do not simply increase the number: you may collide with future official kernel release.--- debian/config/defines.orig 2013-04-23 18:44:09.560859905 +0200 +++ debian/config/defines 2013-04-23 18:43:42.772860608 +0200 @@ -1,5 +1,5 @@ [abi] -abiname: 4 +abiname: 4fix ignore-changes: module:net/l2tp/* # A bunch of NFS/SunRPC exports, not selected by module because MIPS has
 If you want to play with kernel config then first prepare the source tree:
If you want to play with kernel config then first prepare the source tree:
$ fakeroot debian/rules source
$ fakeroot make -f debian/rules.gen setup_i386_none_686-pae
- If you have ready-to-use
.configfile, copy it to kernel source tree:
$ cp /boot/config-3.2.0-4-686-pae debian/build/build_i386_none_686-pae/.config - If you want to configure the kernel, run:
$ make -C debian/build/build_i386_none_686-pae menuconfig
- Now run compilation:
$ fakeroot make -f debian/rules.gen binary-arch_i386_none_686-pae  If you want to build
If you want to build linux-headers-XXX-commonpackage:
$ fakeroot make -f debian/rules.gen binary-arch_i386_none_real- To clean do:
$ make -f debian/rules clean
Another way (not tested):
cp /boot/config-3.2.0-4-686-pae .config
make menuconfigmake-kpkg --rootcmd fakeroot --initrd -j`grep ^processor /proc/cpuinfo|wc -l` linux-imagemake-kpkg --rootcmd fakeroot --initrd -j`grep ^processor /proc/cpuinfo|wc -l` linux-headers
Relevant links:
-
- Creating custom kernels with Debian's kernel-package system – build kernel with Debian patches from original sources.
- To enable
linux-patch-debianlogocheck for[*] Debian GNU/Linux Open Use logokernel configuration option (see Tux Logo during booting
fakeroot make-kpkg --append-to-version=.20130123linux-image-686-paekernels in Debian repo
How to submit a kernel patch?
- create branch e.g.
fix, make changes, commit them git format-patch master..fixscripts/checkpatch.pl --strict 0001-myfix.patch
Send using Thunderbird, but apply the following settings:
mailnews.send_plaintext_flowed=falsemailnews.wraplength=0mailnews.reply_in_default_charset=true(Display → Advanced → When possible use the default character encoding in replies)
Read:
Can I use variable substitution in debian/control file?
TLS_CACERTDIR is not used by GNUtls which is used by ldap-utilsca-certificates package, so more secure is to add a link to /usr/share/ca-certificates and append file name to /etc/ca-certificates.confbadblocks -w -t random -v -o badblocks-sda /dev/sda"Девица не хочет лезть в Окно" – device not compatible with Windows.