Database
- Deferred Integrity Constraints, Deferred Integrity Constraints in Oracle8 – this feature allows to insert child rows prior to parent rows while integrity is checked on commit.
Transaction principles (ACID)
- Atomicity — операция либо целиком выполняется полностью изменяя данные, либо отменяется и не оставляет за собой следов.
- Consistency (integrity) — после того как приложение выполняет операцию ее результат становится доступным для всех последующих операций.
- Isolation — операции одних пользователей не имеют побочных эффектов на других пользователей.
- Durability — изменения сделанные в результате успешной опрации сохраняют результат даже в случае системного сбоя.
Transaction isolation levels
The isolation level measures concurrent transactions' capacity to view data that have been updated, but not yet committed, by another transaction. If other transactions were allowed to read data that are as-yet uncommitted, those transactions could end up with inconsistent data were the transaction to roll back, or end up waiting unnecessarily were the transaction to commit successfully.
Depending on isolation level the following phenomena are permissible1):
- Lost update
Two transactions both update a row and then the second transaction aborts, causing both changes to be lost. This occurs in systems that don’t implement any locking. The concurrent transactions aren’t isolated. - Dirty read
One transaction reads changes made by another transaction that hasn’t yet been committed. This is very dangerous, because those changes might later be rolled back. - Unrepeatable read
A transaction reads a row twice and reads different state each time. For example, another transaction may have written to the row, and committed, between the two reads. - Second lost updates problem
A special case of an unrepeatable read. Imagine that two concurrent transactions both read a row, one writes to it and commits, and then the second writes to it and commits. The changes made by the first writer are lost. - Phantom read
A transaction executes a query twice, and the second result set includes rows that weren’t visible in the first result set. (It need not necessarily be exactly the same query.) This situation is caused by another transaction inserting new rows between the execution of the two queries.
A higher isolation level means less concurrence and a greater likelihood of performance bottlenecks, but also a decreased chance of reading inconsistent data. A good rule of thumb is to use the highest isolation level that yields an acceptable performance level. The following are common isolation levels, arranged from lowest to highest:
- Read uncommitted: Data that have been updated but not yet committed by a transaction may be read by other transactions.
On this level no locks are possible, as the data is available for reading just after modification. Rolling back the transaction will, however, revert the modifications.
Permits dirty reads but not lost updates. One transaction may not write to a row if another uncommitted transaction has already written to it. Any transaction may read any row, however. This isolation level may be implemented using exclusive write locks. - Read committed: Only data that have been committed by a transaction can be read by other transactions.
On this level as well as next level the transaction can lock the data viaSELECT … FOR UPDATEexplicitly. Updated and removed rows are implicitly locked.
Permits unrepeatable reads but not dirty reads. This may be achieved using momentary shared read locks and exclusive write locks. Reading transactions don’t block other transactions from accessing a row. However, an uncommitted writing transaction blocks all other transactions from accessing the row.
- Repeatable read: Only data that have been committed by a transaction can be read by other transactions, and multiple reads will yield the same result as long as the current transaction has not been committed.
Permits neither unrepeatable reads nor dirty reads. Phantom reads may occur. This may be achieved using shared read locks and exclusive write locks. Reading transactions block writing transactions (but not other reading transactions), and writing transactions block all other transactions. - Serializable: This, the highest possible isolation level, ensures a transaction's exclusive read-write access to data. It includes the conditions of read committed and repeatable read and stipulates that all transactions run serially to achieve maximum data integrity. This yields the slowest performance and least concurrency.
On this level allSELECTstatements will lock the matched rows for writing (e.g.SELECT … LOCK IN SHARE MODE), so another transaction can still read the data, but not modify it.
Provides the strictest transaction isolation. It emulates serial transaction execution, as if transactions had been executed one after another, serially, rather than concurrently. Serializability may not be implemented using only row-level locks; there must be another mechanism that prevents a newly inserted row from becoming visible to a transaction that has already executed a query that would return the row.
Feature comparison
| Title | MySQL | HSQL | DB2 | MSSQL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Show query execution plan | EXPLAIN SELECT ... | EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT ... | EXPLAIN SELECT ... | SET SHOWPLAN_ALL ON; 2) |
Number of characters that can actually be stored in VARCHAR column |
|
|
|
|
| Get last generated primary key | SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() | CALL IDENTITY() | VALUES IDENTITY_VAL_LOCAL() | SELECT @@IDENTITY |
Limit the number of result rows of SELECT statement to X rows | SELECT … LIMIT X | SELECT … LIMIT X | SELECT … FETCH FIRST X ROWS ONLY | SELECT … OFFSET 0 FETCH FIRST X ROWS ONLY |
ON UPDATE CASCADE for foreign keys |  Using FOREIGN KEY Constraints Using FOREIGN KEY Constraints |  Referential constraint definition Referential constraint definition |  FOREIGN KEY rule-clause FOREIGN KEY rule-clause |  Cascading Referential Integrity Constraints Cascading Referential Integrity Constraints |
GROUP BY ROLLUP syntax | GROUP BY col1, col2, … WITH ROLLUP7) |  (check forum). As workaround use (check forum). As workaround use UNION of several SELECT statements. | GROUP BY ROLLUP(col1, col2, …)8) | GROUP BY ROLLUP(col1, col2, …) |
GROUP BY CUBE syntax |  |  | GROUP BY CUBE(col1, col2, …) | GROUP BY CUBE(col1, col2, …) |
Calculate difference between two dates (date2 - date1) in seconds | TIMESTAMPDIFF(second, date1, date2) | DATEDIFF('second', date1, date2) | TIMESTAMPDIFF(2, TIMESTAMP(date2) - TIMESTAMP(date1))9) | DATEDIFF(second, date1, date2) |
| Convert date to UNIX/POSIX timestamp | UNIX_TIMESTAMP(date) | UNIX_TIMESTAMP(date) | CAST (DAYS(date) - DAYS('1970-01-01') AS INTEGER) * 86400 + MIDNIGHT_SECONDS(date) | DATEDIFF(second, '1970-01-01', date) |
| Validation query (see also here) | SELECT 1 | SELECT 1 FROM information_schema.system_users | VALUES 1 | SELECT 1 |
IBM DB2
DB2 drawbacks:
- Does not support
UNSIGNEDnumeric types. - Does not support
DATETIME(non-SQL standard). UseTIMESTAMPinstead. - Does not support
TINYINT(non-SQL standard) type. - Does not support
BOOLEANtype, thus boolean type should be emulated on number type and queries should be re-written (where A and Bwill not work, could beWHERE A <> 0 AND B <> 0). - Does not support indexes on varchar greater then 1024 (otherwise SQLSTATE 54008 is returned).
- Varchar stores in bytes, thus there is a string overfit/truncation issue.
- Error reporting is not user-friendly unless message error codes are resolved.
- Row locks issues. See How to avoid deadlocks.
- Manual table page size management. If accumulated size of columns exceeds 4K, then table page size should be increased (see Choosing a page size).
- Claims to support
/* */-comments (check SQL comments), but it turned out to be a feature of SQL-console. CREATE PROCEDUREandCREATE TRIGGERstatements should end with@delimiter, and not with;like other SQL statements may.
How to reorganize a table (REORG table)?
50918 is the port number):
db2 => CATALOG TCPIP NODE that_node REMOTE db2_hostname SERVER 50918 DB20000I The CATALOG TCPIP NODE command completed successfully. db2 => CATALOG DATABASE remote_db AS db_alias AT NODE that_node DB20000I The CATALOG DATABASE command completed successfully. db2 => CONNECT TO db_alias USER my_user USING **** Database Connection Information ... db2 => REORG TABLE db_alias.table_name DB20000I The REORG command completed successfully.
How to add an identity column (primary key) to an existing table?
ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME ADD COLUMN id INTEGER NOT NULL WITH DEFAULT 0 ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME ALTER COLUMN id DROP DEFAULT ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME ALTER COLUMN id SET GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY REORG TABLE TABLE_NAME UPDATE TABLE_NAME SET id = DEFAULT ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME ALTER COLUMN id SET PRIMARY KEY
It might happen that something will go wrong with above. Then consider the alternative of creating a new table plus copying all data from old table to new one.
How to rename a table?
RENAME TABLE TABLE_NAME TO new_table_name
however if table has a foreign key constraint or another table refers it, this command will fail. So you need to drop these constrains first. The list of them you can find in a table SYSCAT.REFERENCES:
SELECT * FROM syscat.references WHERE tabname = 'table_name' ALTER TABLE TABLE_NAME DROP CONSTRAINT table_name_fk
How concatenate INTEGER and VARCHAR ?
CONCAT() function fails to concatenate string and integer. Something like SELECT text_column || ' (' || number_column || ')' FROM … results the following error:
DB2 SQL Error: SQLCODE=-440, SQLSTATE=42884, SQLERRMC=||;FUNCTION No routine was found with the specified name and compatible arguments.
CONCAT(). The normal casting like CAST(number_column AS CHAR(10)) or CAST(number_column AS VARCHAR(1024)) do not work. The solution is:SELECT text_column || ' (' || RTRIM(CHAR(number_column)) || ')' FROM ...
Another solution:
SELECT VARCHAR(CAST(number_column AS CHAR)) || text_column FROM TABLE
On MSSQL:
SELECT CAST(number_column AS VARCHAR) + text_column FROM TABLE
How to learn what SQL statement and what connection is holding a lock on the table (which causes SQLSTATE=40001 error)? How to select from the table in non-blocking mode?
db2 => CONNECT TO db_alias USER my_user USING **** Database Connection Information ... db2 => ATTACH TO that_node USER my_user USING **** Instance Attachment Information ... db2 => GET SNAPSHOT FOR LOCKS ON db_alias Database Lock Snapshot ... List Of Locks Lock Name = 0x02000D000401B0110000000052 Lock Attributes = 0x00000008 Release Flags = 0x40000000 Lock Count = 1 Hold Count = 0 Lock Object Name = 296747268 Object Type = Row Tablespace Name = USERSPACE1 Table Schema = DB_ALIAS Table Name = TABLE_NAME Mode = X
See also:
- DB2_SKIPINSERTED registry variable or use
SELECT … WITH UR('Uncommitted Read'). Also see Lock avoidance in DB2 UDB V8
How to avoid deadlocks?
com.ibm.db2.jcc.a.pn: The current transaction has been rolled back because of a deadlock or timeout. Reason code "2".. SQLCODE=-911, SQLSTATE=40001, DRIVER=3.52.95
Also posted as Parallel inserts cause deadlock on DB2.
- Increase lock list space or set it to
AUTOMATIC:db2 "update db cfg using LOCKLIST 3200 AUTOMATIC" db2 "update db cfg using MAXLOCKS 60 AUTOMATIC"
- Commit more frequently.
See also:
Is there any analogue of MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function in DB2?
XMLAGG() (taken from Create a delimited string from a query in DB2).
SELECT group_column, SUBSTR(XMLSERIALIZE(XMLAGG(XMLTEXT(CONCAT(', ', concat_column))) AS VARCHAR(1024)), 3) FROM TABLE_NAME GROUP BY group_column
How enable logging for DB2 JDBC driver?
jdbc:db2://db2server:50012/MYDB:traceFile=c:/jdbc.log;TraceLevel=TRACE_ALL;
How to make SQL error codes resolved to text messages?
- Enable
retrieveMessagesFromServerOnGetMessageJDBC property:jdbc:db2://db2server:50012/MYDB:currentSchema=MYSCHEMA;retrieveMessagesFromServerOnGetMessage=true; - Create
SYSIBM.SQLCAMESSAGECCSIDstored procedure.
Afterwards the SQLException.getMessage() will resolve the numeric code to text message, for example: "MYSCHEMA.DUMMY_TABLE" is an undefined name.. SQLCODE=-204, SQLSTATE=42704, DRIVER=3.52.95
SQLCAMESSAGECCSID results SQLCODE=-1042 SQLSTATE=58004 error, check that DB2_FMP_COMM_HEAPSZ10) registry variable is not set to 0. In this case either remove this variable to use the default value. Check here for more information.
How to specify the transaction isolation level for DB2 JDBC driver?
defaultIsolationLevel parameter. The value is one from java.sql.Connection constants:
<bean id="dbDataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:db2://db2server:50012/my_db:currentSchema=MY_SCHEMA;defaultIsolationLevel=2;" /> <property name="validationQuery" value="values 1" /> <property name="username" value="my_user" /> <property name="password" value="my_pass" /> </bean>
Where can I download latest JDBC drivers?
MS SQL
How to view queries that are blocked?
SELECT tl.request_session_id [waitingSeesionID], wt.blocking_session_id [blockingSessionID], wt.resource_description, wt.wait_type, wt.wait_duration_ms, db_name (tl.resource_database_id) [DB], tl.resource_associated_entity_id [WaitingAssEntity], tl.resource_type, wrt.[text] [Waiting_TSQL], btl.request_type [BlockingReqType], brt.[text] [Blocking_TSQL] FROM sys.dm_tran_locks tl JOIN sys.dm_os_waiting_tasks wt ON tl.lock_owner_address = wt.resource_address JOIN sys.dm_exec_requests wr ON wr.session_id = tl.request_session_id CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(wr.sql_handle) AS wrt LEFT JOIN sys.dm_exec_requests br ON br.session_id = wt.blocking_session_id OUTER APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(br.sql_handle) AS brt LEFT JOIN sys.dm_tran_locks AS btl ON br.session_id = btl.request_session_id
How to avoid deadlocks?
- Modify non-clustered index locking behaviour.
Page level locking is often associated with non-clustered indexes. This can create a problem because page locks prevent rows being accessed on the page by other transactions. Thus non clustered index usage may introduce extra locking overhead on a table. To get around this and reduce the index locking overhead you can direct the index to lock at row level.ALTER INDEX myindex ON mytable SET ( ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON );
Or more extreme:
ALTER INDEX myindex ON mytable SET ( ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = OFF );
- Disable table page lock escalation (also see Lock Escalation):
ALTER TABLE my_table SET ( LOCK_ESCALATION = DISABLE );
- Change transaction isolation level to
READ UNCOMIITTED. - Use Snapshot Isolation.
Are DDL statements transactional?
How to connect to MSSQL server from Perl?
- Install
libiodbc-dev. - Install
krb5-dev/libkrb5-devand (comerr-dev/libcom_err-dev). - Download FreeTDS tarball, unpack it.
- In case you have compiled above libraries from sources run:
CPPFLAGS=-I$HOME/include ./configure –prefix=$HOME –with-iodbc=$HOME –enable-krb5=gssapi_krb5 - Then
make all install - Install
DBI:
perl -MCPAN -Mlocal::lib -I~/perl5 -e "install DBI" - Install
DBD::Sybase:
SYBASE=$HOME perl -MCPAN -I~/perl5 -Mlocal::lib -e 'notest("install", "DBD::Sybase")'
Issues:
- FreeTDS supports passwords no longer then 30 characters (check here and there, bug#706388). Apply this patch:
--- ./include/tds.h 2013-04-26 11:17:07.000000000 +0200 +++ ./include/tds.h.orig 2012-07-17 10:16:16.000000000 +0200 @@ -499,7 +499,7 @@ #define TDS_ALIGN_SIZE sizeof(tds_align_struct) -#define TDS_MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ 50 +#define TDS_MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ 30 typedef struct tds_login { DSTR server_name; /**< server name (in freetds.conf) */
DBD::Sybasesupports passwords no longer then 32 characters (check bug#706392). Apply this patch:--- dbdimp.h.orig 2013-04-03 22:16:20.000000000 +0200 +++ dbdimp.h 2013-04-29 17:24:21.000000000 +0200 @@ -51,6 +51,9 @@ #define MAX_SQL_SIZE 255 +/* The same as TDS_MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ */ +#define MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ 50 + /* Define dbh implementor data structure */ struct imp_dbh_st { dbih_dbc_t com; /* MUST be first element in structure */ @@ -71,8 +74,8 @@ int lasterr; int lastsev; - char uid[32]; - char pwd[32]; + char uid[MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ]; + char pwd[MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ]; char server[64]; char charset[64]; --- dbdimp.c.orig 2013-04-03 22:16:20.000000000 +0200 +++ dbdimp.c 2013-04-29 17:24:56.000000000 +0200 @@ -1147,10 +1147,10 @@ imp_dbh->server[63] = 0; } - strncpy(imp_dbh->uid, uid, 32); - imp_dbh->uid[31] = 0; - strncpy(imp_dbh->pwd, pwd, 32); - imp_dbh->pwd[31] = 0; + strncpy(imp_dbh->uid, uid, MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ); + imp_dbh->uid[MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ - 1] = 0; + strncpy(imp_dbh->pwd, pwd, MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ); + imp_dbh->pwd[MAX_LOGIN_STR_SZ - 1] = 0; sv_setpv(DBIc_ERRSTR(imp_dbh), "");
Second option is Easysoft ODBC driver (example in How do I connect to a MSSQL database using Perl's DBI module?).
MySQL
How rename a database?
RENAME DATABASE was added in MySQL 5.1.7 but was found to be dangerous and was removed in MySQL 5.1.23. An alternative way is:
for table in `mysql -uroot -s -N -e "show tables from old_db"`; do mysql -uroot -s -N -e "rename table old_db.$table to new_db.$table;"; done
however it does not work if any of tables has a trigger (results Trigger in wrong schema error). In such case use more universal but more slow approach:
mysqldump old_db | mysql -uroot new_db mysql -uroot -e 'drop database old_db'
mysqldump: Error 2013: Lost connection to MySQL server during query when dumping table ...
/etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf so that it includes:
[mysqld] net_read_timeout=300 net_write_timeout=300
and restart mysql (/etc/init.d/mysql restart). There is a request to allow to set these properties for mysqldump for a particular session but still not implemented, hence can only be set globally.
How to change default pager for mysql client?
[client] pager = less -qniRSFX -# 20
For coloring the output, check Разукрашиваем вывод mysql-client в консоли and MySQL command line pager & mysmartpager (download pages: grc, percona-toolkit and all-in-one).
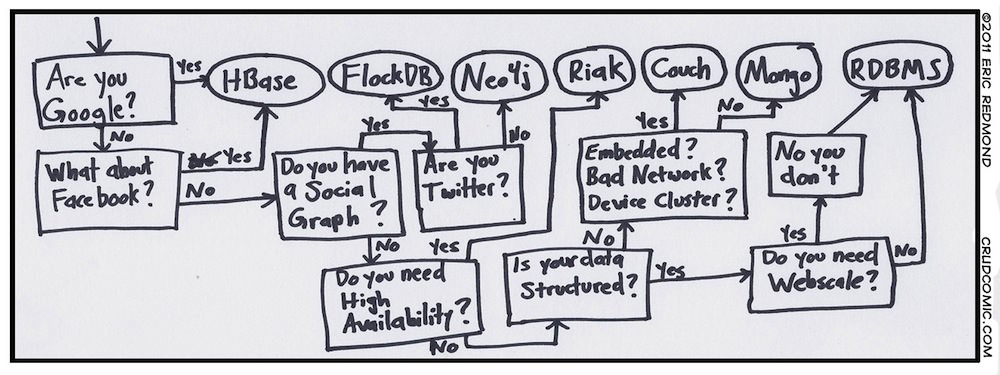
Big Data
- Big Data головного мозга – обзор продуктов ASF, которые продают под соусом Big Data (Storm, Sqoop и т.п.), МРР-движков поверх HDFS (Impala, Dill, Kudu), традиционных аналитических MPP-систем (Teradata, Vertica, GPDB и т.п.).
Apache Lucene / Elasticsearch:
JDBC datasource Spring configuration examples
Pooled MySQL datasource
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close" p:driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" p:jdbcUrl="jdbc:mysql://host:3306/my_db?autoReconnect=true" p:user="john" p:password="john_pass" p:maxPoolSize="20" p:maxStatements="50" p:testConnectionOnCheckin="true" p:idleConnectionTestPeriod="7200" p:preferredTestQuery="SELECT 1" />
Pooled HSQL datasource
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource" destroy-method="close" p:driverClassName="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver" p:url="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:test" p:username="sa" p:password="" p:maxActive="20" p:testOnReturn="true" p:testWhileIdle="true" p:validationInterval="1800000" p:validationQuery="SELECT 1 FROM information_schema.tables" />
Embedded HSQL server
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.1.xsd"> <jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" /> </beans>
JNDI source
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.1.xsd"> <jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="java:jdbc/myDS" /> </beans>